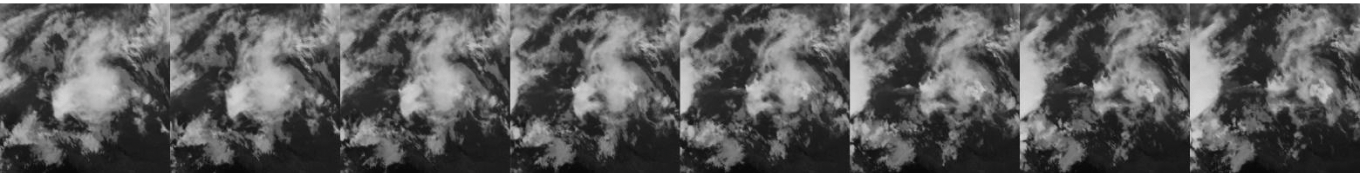
Efficient operation of solar power plants requires accurate and fast weather forecasting, which enables effective management of unexpected weather changes. Our satellite imagery-based, AI-powered forecasting system provides a significant advancement in this area.

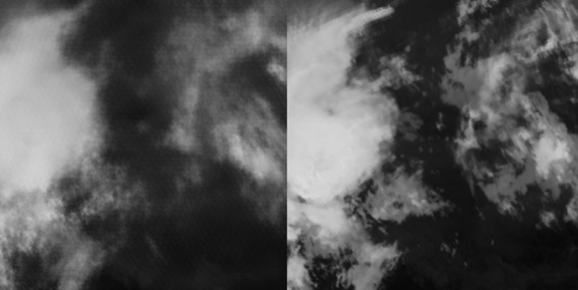
Here you can see the AI model’s prediction compared to the actual cloud movement.

| Week start | Week end | PSNR | MSE | SSIM | LPIPS | FID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-02-17 | 2025-02-24 | 24.9646 | 245.915813 | 0.8244 | 0.1252 | 58.44 |
| 2025-02-24 | 2025-03-03 | 22.0934 | 439.907506 | 0.6685 | 0.2011 | 67.77 |
| 2025-03-03 | 2025-03-10 | 25.2581 | 284.396000 | 0.7843 | 0.1351 | 64.35 |
| 2025-03-10 | 2025-03-16 | 18.1584 | 1029.854917 | 0.5399 | 0.2774 | 97.68 |
| Week start | Week end | PSNR | MSE | SSIM | LPIPS | FID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2025-02-17 | 2025-02-24 | 29.8997 | 72.874530 | 0.8822 | 0.1229 | 48.09 |
| 2025-02-24 | 2025-03-03 | 25.9315 | 176.918294 | 0.7757 | 0.1894 | 54.20 |
| 2025-03-03 | 2025-03-10 | 28.1371 | 360.669998 | 0.8377 | 0.1386 | 57.85 |
| 2025-03-10 | 2025-03-16 | 19.4334 | 1419.678690 | 0.6155 | 0.2994 | 72.88 |
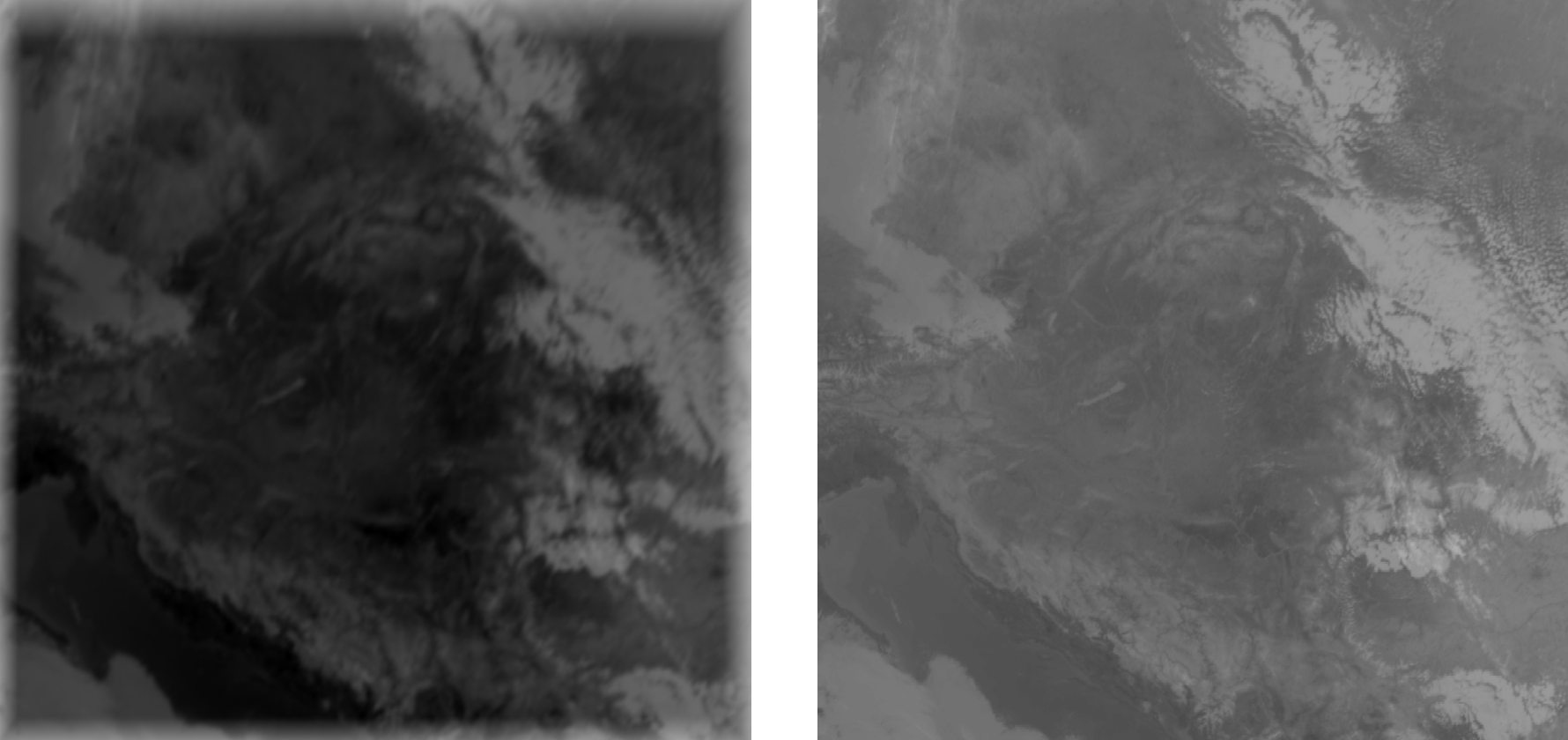
2025.02.20 13:00 original
Predicted
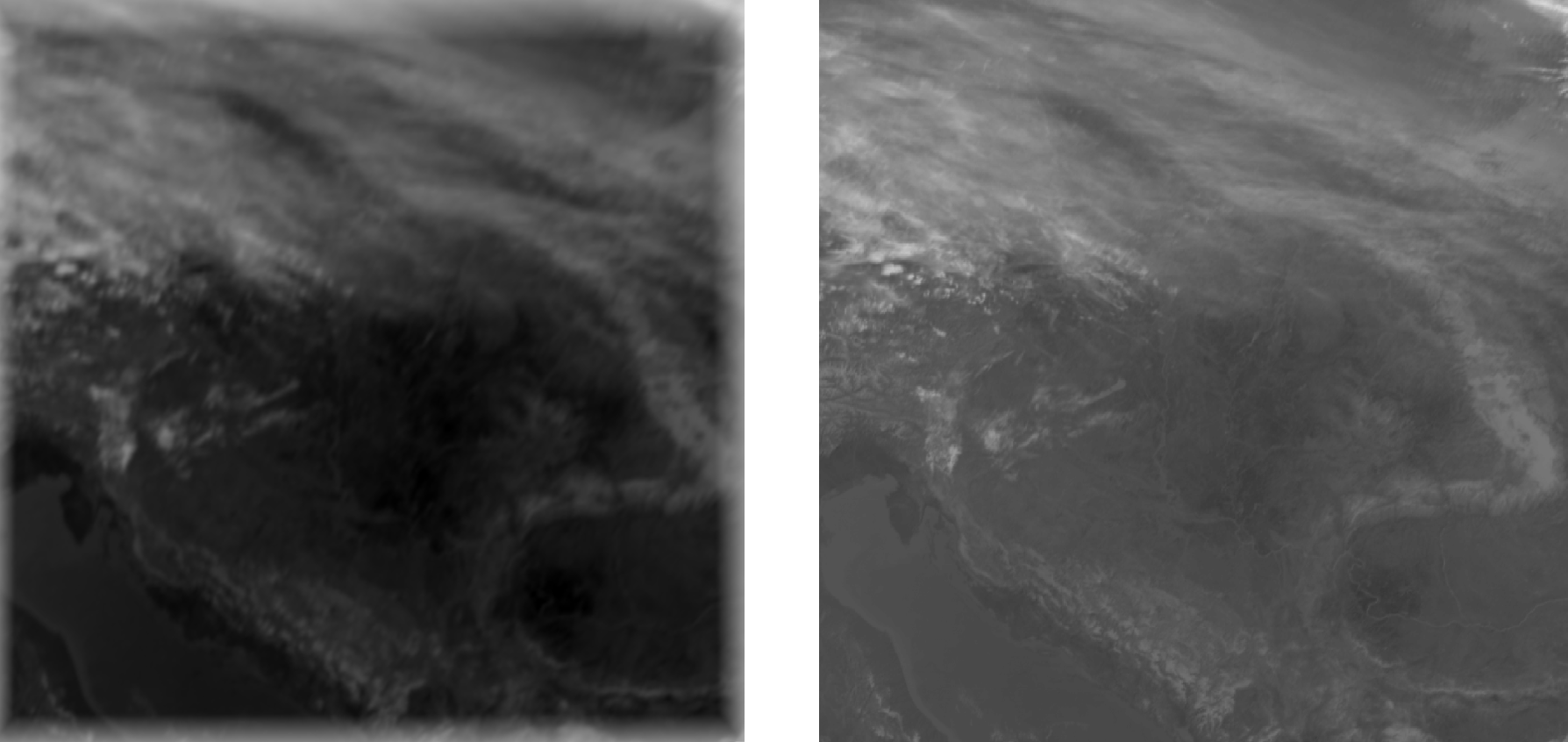
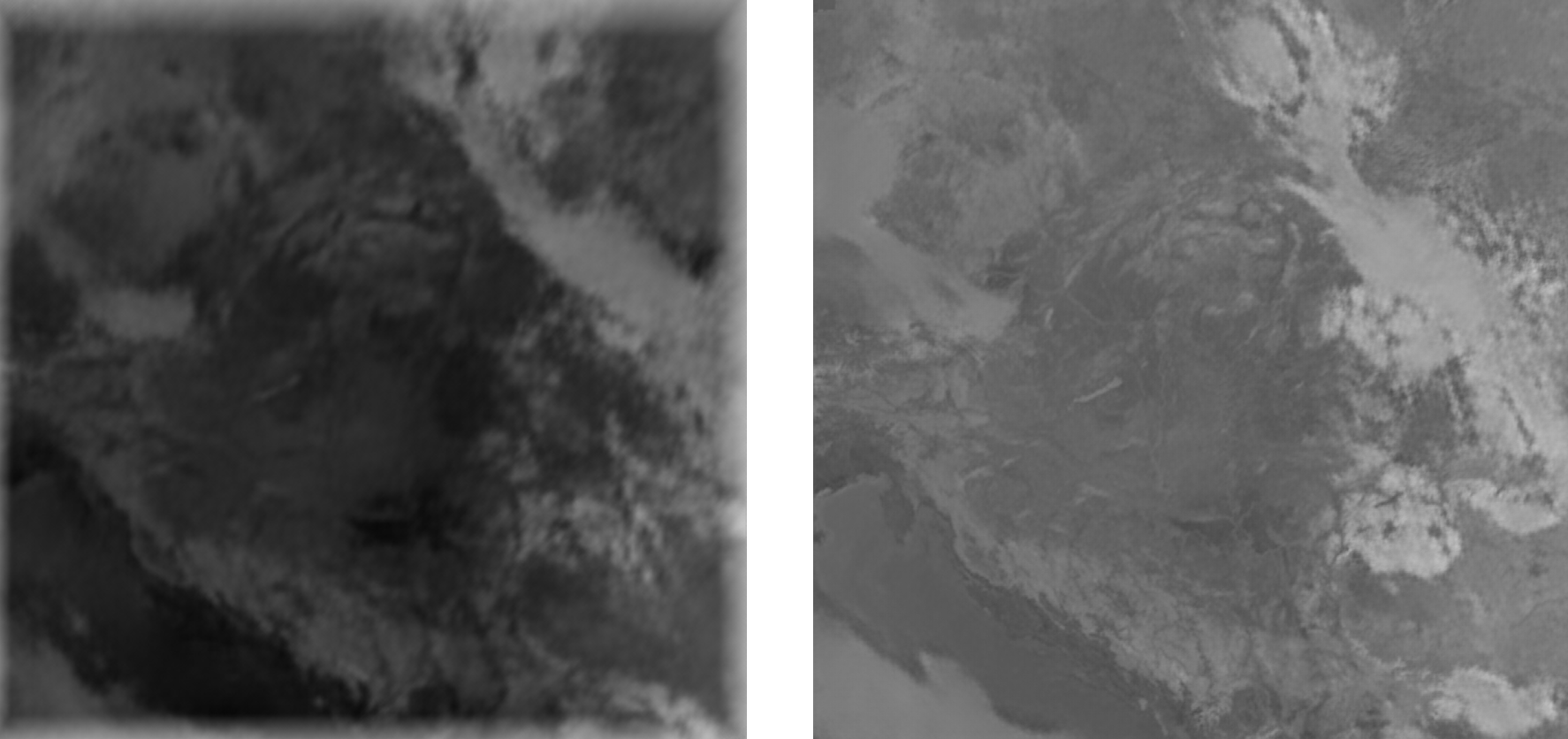
2025.03.04 09:00 original
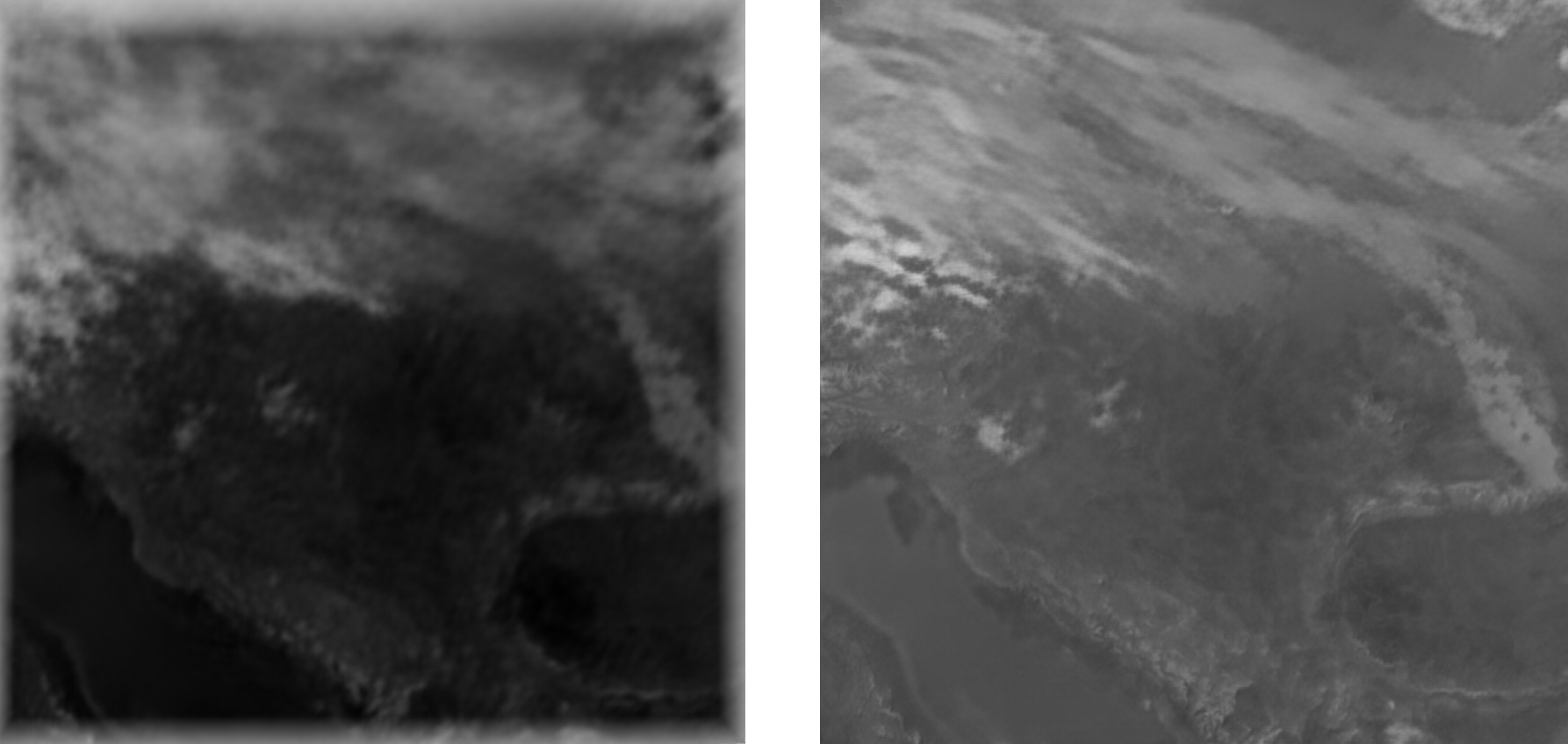
Predicted
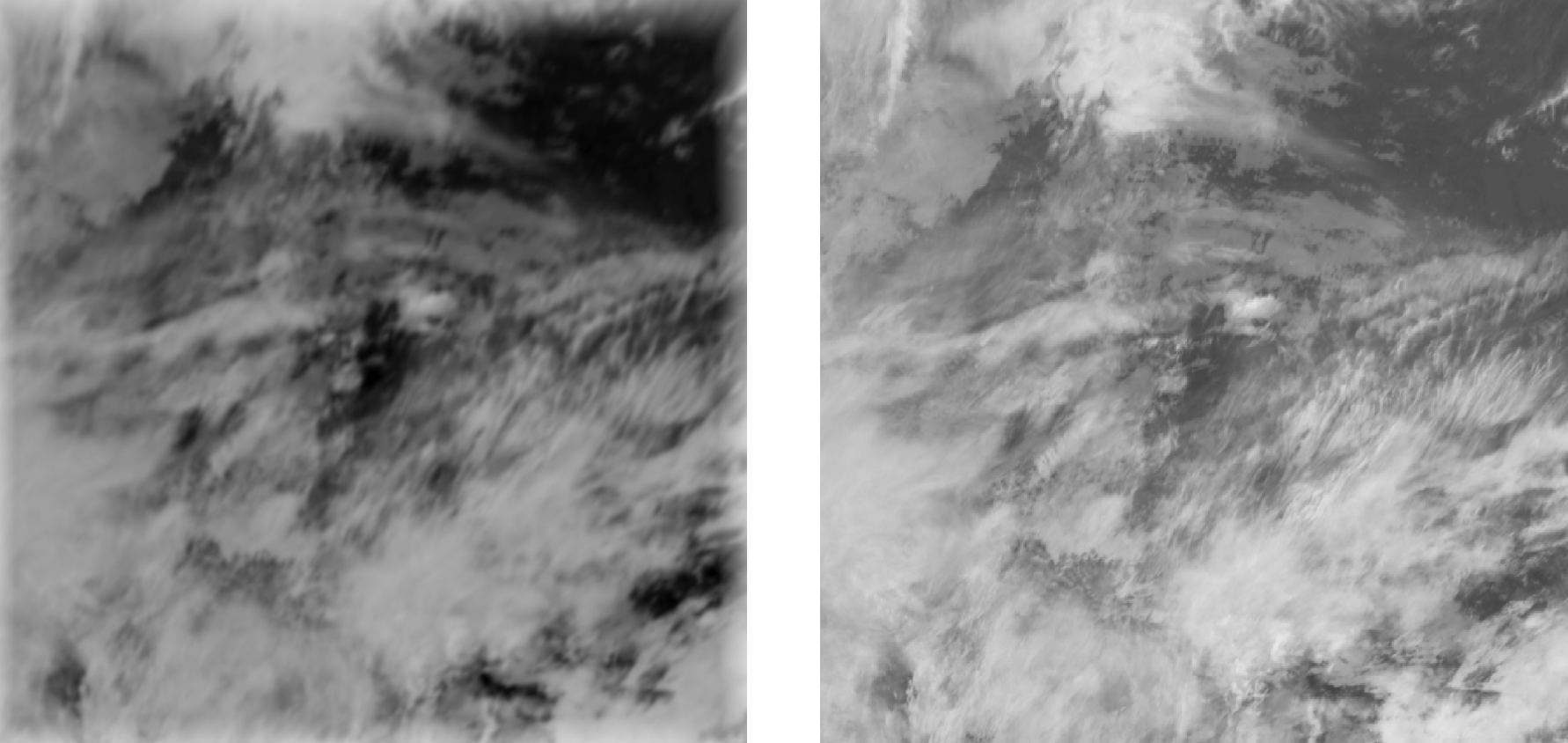
2025.03.12 16:00 original
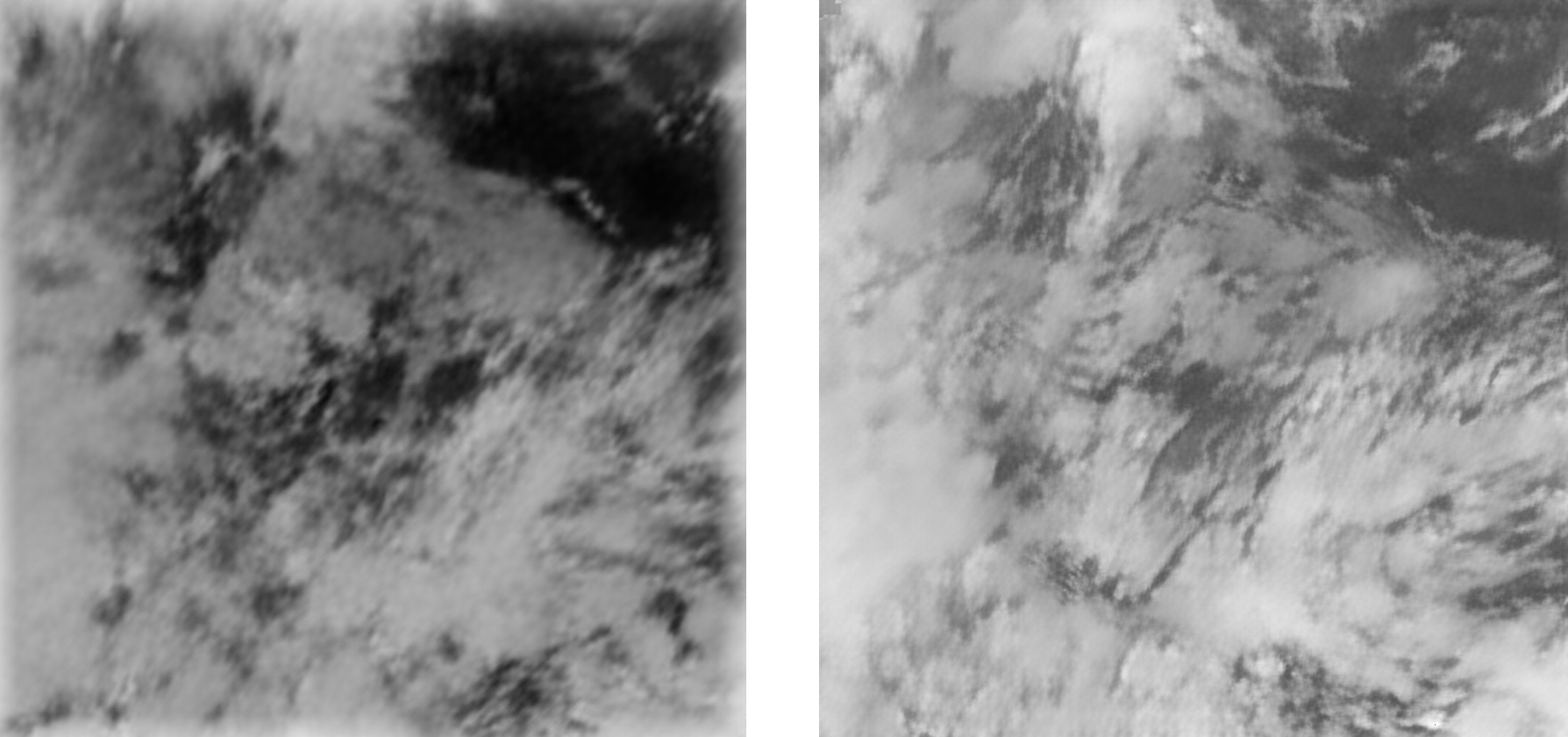
Predicted